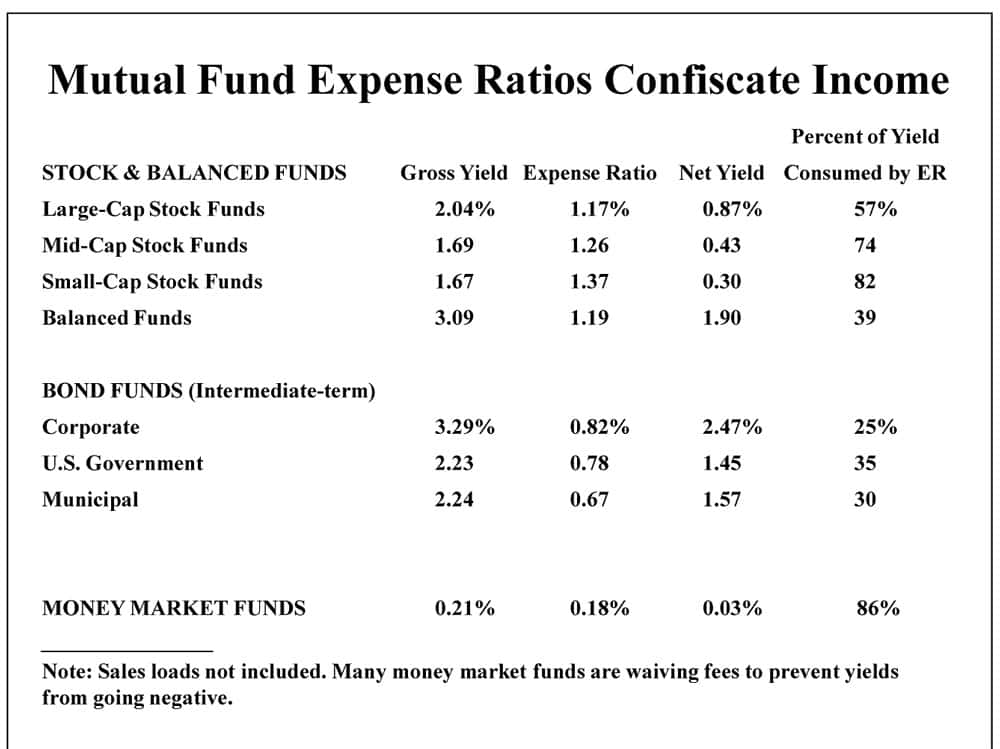
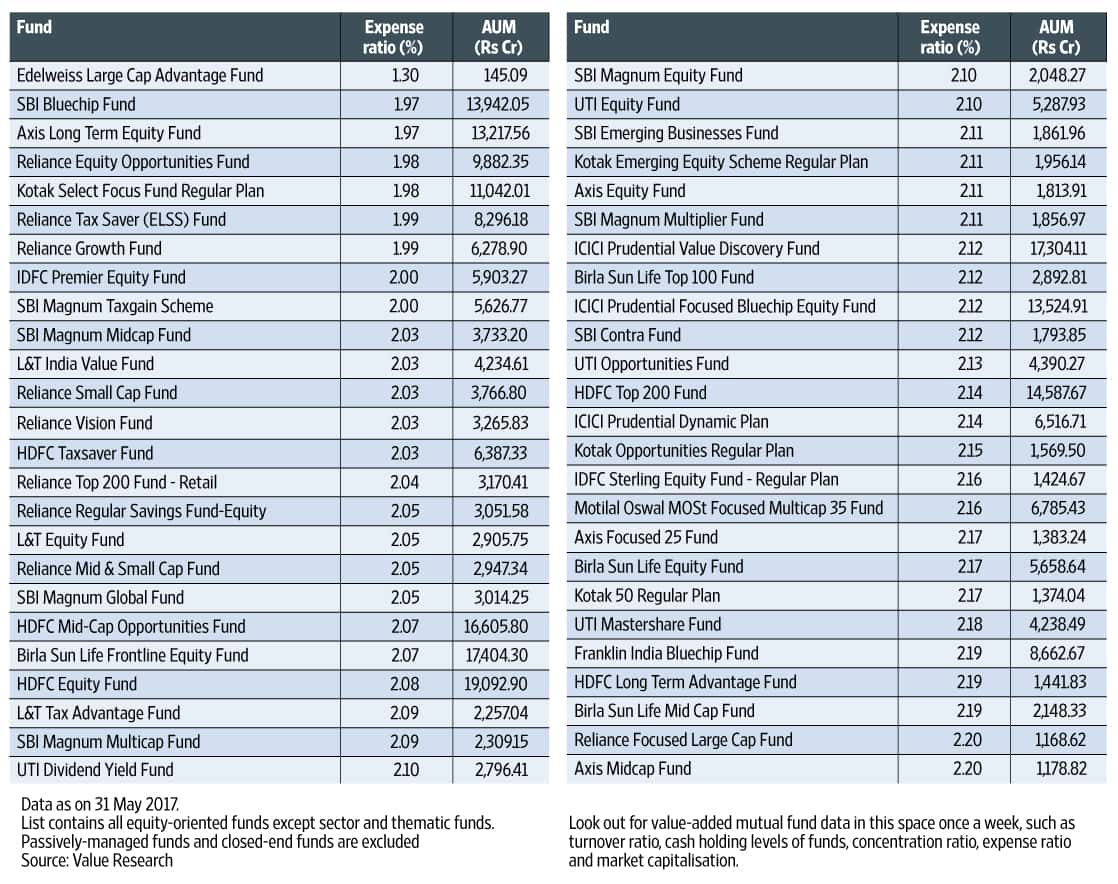
Learn about mutual fund expense ratio examples and how they impact your investments. This article covers everything you need to know about mutual fund fees and expenses.
Mutual funds are popular investment vehicles for individual and institutional investors alike. They provide diversification, professional management, and easy accessibility to a broad range of assets. However, investing in mutual funds comes with costs, and one of the essential metrics to consider is the mutual fund expense ratio.
In this article, we’ll explore mutual fund expense ratio examples, what they are, how they work, and why they matter for your investment strategy.
What is a Mutual Fund Expense Ratio?
A mutual fund expense ratio is a measure of the fund’s operating expenses as a percentage of its total assets. It includes all the costs associated with managing the fund, such as management fees, administrative expenses, marketing expenses, and other fees. The expense ratio is deducted from the fund’s assets, which reduces the fund’s returns to investors.
For example, if a mutual fund has an expense ratio of 1%, it means that the fund charges investors 1% of their investment every year to cover its expenses. Therefore, if you invest $10,000 in the fund, you’ll pay $100 in fees annually.
Mutual Fund Expense Ratio Examples
Mutual fund expense ratios can vary significantly depending on the type of fund, investment strategy, and management style. Here are some mutual fund expense ratio examples to give you an idea of how different types of funds charge fees:
- Index Funds: Index funds are passive investment vehicles that aim to replicate the performance of a particular market index, such as the S&P 500. They have lower expense ratios than actively managed funds because they require less research and analysis. For example, the Vanguard 500 Index Fund has an expense ratio of 0.14%, which means that it charges investors $14 in fees for every $10,000 invested.
- Actively Managed Funds: Actively managed funds have higher expense ratios than index funds because they require more research, analysis, and decision-making. The fees can range from 0.5% to 2% or more, depending on the fund’s strategy and asset class. For example, the Fidelity Magellan Fund, one of the largest actively managed funds, has an expense ratio of 0.61%, which means that it charges investors $61 in fees for every $10,000 invested.
- Specialty Funds: Specialty funds invest in specific sectors or industries, such as technology, healthcare, or energy. They have higher expense ratios than broad-based funds because they require specialized knowledge and expertise. For example, the T. Rowe Price Health Sciences Fund has an expense ratio of 0.77%, which means that it charges investors $77 in fees for every $10,000 invested.
Why Mutual Fund Expense Ratio Matters
Mutual fund expense ratios may seem like a small percentage, but they can have a significant impact on your investment returns over time. High expense ratios can eat into your returns, especially in the long run. Here’s why mutual fund expense ratio matters:
- Lower returns: High expense ratios can reduce your investment returns, which can impact your ability to achieve your financial goals. For example, if you invest $10,000 in a fund that has a 1% expense ratio and earns a 7% return annually, you’ll have $38,697 after 20 years. However, if you invest in a fund that has a 0.5% expense ratio and earns the same 7% return, you’ll have $44,478 after 20 years.
- Lower risk-adjusted returns: Mutual fund expense ratios can also impact your risk-adjusted returns. Risk-adjusted returns measure how much return you get relative to the amount of risk you take. If a fund has a higher expense ratio, it may not be able to outperform its benchmark index consistently, which means that you may be paying more for the same or lower returns than a low-cost index fund.
- Long-term impact: Over time, the impact of mutual fund expense ratios can compound, leading to a significant difference in your investment outcomes. For example, if you invest $100,000 in a mutual fund that has a 1.5% expense ratio and earns a 5% return annually for 30 years, you’ll end up with $322,472. However, if you invest in a similar fund that has a 0.5% expense ratio and earns the same 5% return, you’ll end up with $458,705. That’s a difference of over $136,000 in your investment returns.
How to Choose a Mutual Fund with a Low Expense Ratio
When selecting a mutual fund, it’s essential to consider the expense ratio as part of your investment criteria. Here are some tips on how to choose a mutual fund with a low expense ratio:
- Look for index funds: Index funds have lower expense ratios than actively managed funds because they require less research and management.
- Consider the fund’s investment objective: Choose a fund that aligns with your investment objectives and risk tolerance.
- Compare the expense ratios: Compare the expense ratios of similar funds to identify the ones with the lowest fees.
- Check for hidden fees: Some mutual funds may charge other fees, such as sales loads, redemption fees, or account maintenance fees. Make sure to read the prospectus and other disclosure documents to understand all the fees associated with the fund.
- Consider tax efficiency: Some mutual funds may have higher expense ratios but offer tax benefits, such as lower capital gains taxes. Consider the tax implications of your investment before making a decision.
In conclusion, mutual fund expense ratio examples are an essential metric to consider when investing in mutual funds. They can impact your investment returns, risk-adjusted returns, and long-term outcomes. By choosing a mutual fund with a low expense ratio, you can reduce your costs and increase your investment returns. Remember to do your research, compare the fees, and consider all the factors that may impact your investment outcomes.